2008 年 12 月(神戸)、熊本大・谷時雄教授とともに「細胞核内ドメイン構造とその生物学的役割」のタイトルを掲げてシンポジウムをオーガナイズしました。開催趣旨と S1-1 タンンパク質についての発表内容はつぎの様なものでした。
シンポジウム開催趣旨
今まで明らかにされてきた細胞核内のコンパートメント( nuclear domains )は、リボソームを合成する核小体をはじめとして 10 以上にもなる。核内ドメインは膜を持たず、構造は動的であり、固有の遺伝子発現過程に関わる特定のタンパク質や RNP 複合体がひっきりなしに出入りしている。そしてこれらのドメインは細胞核反応の選択的効率化とたえず変動する遺伝子発現に応答するための仕掛けを構成していると考えられる。しかし個々の domain についてみると、課題が横たわり解明すべき問題点は多い。本シンポジュウムではこれらコンパートメントの構成要素、ドメインの機能と繰り広げられる反応、ドメインの構築原理、ダイナミックス、そして今後の課題を概観する。このセッションを通して細胞核内ドメインについてさらなる理解が得られることを期待する。 オーガナイザー:井上 晃(大阪市大院・医・分子制御生物)、谷 時雄(熊本大院・自然科学・生命科学)
シンポジウムでの発表要旨:「S1-1 核内ドメイン」以前に見出していた S1-1 はがんへの関わりが強く示唆される核内の RNA 結合タンパク質である。ここでは特徴的な核内存在様式を中心にその細胞生物学的、生理・病理学的意義を考える。 S1-1 は核小体外の数百のダイナミックな斑点状構造体 ( S1-1 核内ドメイン ) に存在し、その 10-40 個は ≧ 0.5 μ m の大きさで S1-1 抗体に強い免疫染色性を示す( S1-1 nuclear bodies: NBs )。 S1-1 ドメインは様々な細胞に共通し、 heat-shock や血清飢餓、細胞の高密度状態、あるいは pol II 阻害など細胞の転写活性の低下時にはその NBs は S1-1 をさらに集積する。一方、小さなドメイン ( S1-1 granules ) は対照的に減衰する。これらの変化は可逆的で通常の培養条件下でもとに戻る。さらに splicing 反応を特異的に阻害した場合も同じドメイン変化が起きる所から S1-1 の splicing への関わりが示唆される。実際、単離 spliceosome 複合体に同定された 311 種のタンパク質中に S1-1 (RBM10) が見出される。 S1-1 NBs は splicing 因子群を集めた nuclear speckles に隣接する位置を占めるが、既知の paraspeckles とは一致せず、微量注入した pre-mRNA を ( 転写阻害時に ) 蓄積する transcription-inactivation dependent RNA domains ( TIDRs )に一致する。したがって S1-1 NBs は、細胞の転写/ splicing 低下時に S1-1 や一群の pre-mRNAs を貯蔵するドメインと考えられる。一方、小さなドメイン群の S1-1 granules は、転写と splicing 反応の場をなす perichromatin fibrils に相当する構造上にあることが免疫電顕で示される。 S1-1 は肺がんのがん抑制遺伝子産物、 RBM5 、のパラログである。また乳がんで顕著に高発現することが示されている。さらに別の NBs を作る前骨髄性白血病のがん抑制遺伝子産物、 PML 、とは分子構造が良く類似する。これらは S1-1 が発がんに関わることを強く予測させる。実際、 siRNA や Tet-On の実験から S1-1 は細胞死の抑制に働く事が判った。ここでは S1-1 と splicing 反応そして発がんの関連性を議論する。
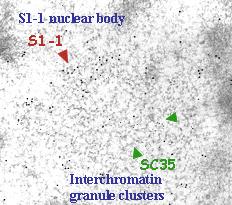 |
転写や splicing 反応の低下で、 S1-1 nuclear bodies は様々な splicing 因子を貯め込んだ inter-chromatin granule clusters (IGCs = 蛍光顕微鏡下のspeckles) との隣接構造を取る。 |